 Yoga ,a physical therapy in holistic style was originated in India.In the past ,there were only Yogi and Brahman used this training to defeat the sickness.
Yoga Yoga ,a physical therapy in holistic style was originated in India.In the past ,there were only Yogi and Brahman used this training to defeat the sickness.
Yoga
Yoga
Yoga
,a physical therapy in holistic style was originated in India.In the past
,there were only Yogi and Brahman used this training to defeat the sickness.
There
are eight levels of Yoga,clearly spelled out, are as follows:
1.Self-Restraint/ "Yama" This can be best defined as the codes of
behavior that keep the aspirant at peace with the world he lives in, as
well as with himself.
2. Observance/ "Niyama" Observances build on the concepts of self-restraint,
putting those principles into action in daily life.
3.Physical Practice/ "Asana" In the Yoga tradition, physical practice
is most recognizable as the Yoga postures and exercises practiced in a typical
studio, everthing from Sun Salutations to headstands. The majority of these
exercises are stretching in character, but many "Asanas" build incredible
strength.
4.Breathing Exercise/ "Pranayama" Breathing exercises develop the
connection between the cultivation of energy/"Prana" and the breath of the
aspirant.
5.Sense Withdrawal/ "Prathyahara" Sense withdrawal is the pulling
of the five senses back into the mind and the detaching from the various
sense stimuli that the surrounding environment is generating. This level
is considered to be the last level of the foundation necessary to be successful
in the pursuit of a true a spiritual experience in meditation.
6.Concentration/ "Dharana" Concentration is possible once sense withdrawal
has begun. The refocusing of the senses on a single concentration point
continues the inward turning of the mind.
7.Meditation/ "Dhyana" Meditation is the unbroken flow of the mind
on a single point for an extended period. In practice, it can be measured
by counting the numbers of breaths in one's focus on a concentration point,
with or without a mantra.
8.Superconsciousness / "Samadhi" Superconciousness is the state of
"union" that word Yoga directly refers to.
The principles
of Yoga
1.Proper breathing.
This means breathing fully and rhythmically, making use of all the
parts of your lungs to increase your oxygen intake.To inhale ,extended
your stomach.Then Flattened stomach while exhaling.
2.Proper exercise. Practice each manner step by step.Try not to
tense your muscle .
3.Concentration. Try to concentrate yourself.It will be easy for
making meditation.
4.Pause & relax. Pause after doing each manner .Then breathe
slowly to relax yourself. |
 |
The benefits of Yoga
1.Increasing Blood
circulation. Yoga helps to reduce blood disease which is the cause of headache,allergy
and strain.
2.Increasing flexibility.Yoga has positions that act upon the various joints
of the body including those joints that are never really on the ‘radar screen’
let alone exercised.
3.Effective in internal organ. Yoga makes heart , stomach,lung,uterus,liver
and kidney stronger.
4.Anti-aging. Yoga helps to anti-aging and control body shape.
5.Psychological. Yoga is a medical care that help to reduce the psychological
symptom.
Preparation before Yoga
practice
1.Mentally : One must
clearly understand the purpose and aim of yoga before practicing .
2.Set time to practice: It will better to practice daily without stoping
.Mornings and evenings being the best times. In the morning stretch the
muscles and joints, waking up the whole body and giving one energy for the
day. Practice in the evening can eliminate accumulated stress, exhaustion
and tension.
3.Find a good place: When practicing, spread a blanket or mat on the ground
to avoid injury, and wear loose, comfortable clothing. To avoid catching
the wind and cold, pick a place that is peaceful, secluded and warm with
circulating, fresh air. Don't forget to remove unnecessary bracelets, earrings,
rings, ties and the like.
4.Exercise on an empty stomach: It is best to exercise after emptying the
bowels. At least wo hours after eating is okay, as the food should be digested
by then. You should wait half an hour after exercising before eating again,
lest the effectiveness of the practice be diminished.
Remember that pregnant and menstruated
women should take a complete rest from yoga postures, and just practice
sitting meditation.
Yoga postures
1.Sit/Easy
Position – Sukhasana
A starting position that helps focus awareness on breathing and the body;
helps strengthen lower back and open the groin and hips.
Sit cross-legged with
hands on knees. Focus on your breath. Keep your spine straight and push
the sit bones down into the floor. Allow the knees to gently lower. If the
knees rise above your hips, sit on a cushion or block. This will help support
your back and hips. Take 5-10 slow, deep breaths. On the next inhale, raise
your arms over your head. Exhale and bring your arms down slowly. Repeat
5-7 times.
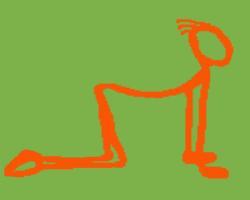 |
2. Dog &
Cat
Begin on your hands and knees. Keep your hands just in front of
your shoulders, your legs about hip width apart. As you inhale,
tilt the tailbone and pelvis up, and let the spine curve downward,
dropping the stomach low, and lift your head up. Stretch gently.
As you exhale, move into cat by reversing the spinal bend, tilting
the pelvis down, drawing the spine up and pulling the chest and
stomach in. Repeat several times, flowing smoothly from dog into
cat, and cat back into dog. |
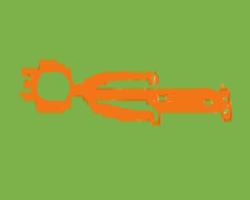
3.Half Shoulderstand
– Ardha Sarvangasana
Promotes proper thyroid function,strengthens abdomen,stretches upper
back,improves blood circulating,induces relaxation.
Lie on your back and lift your legs up into air .Place your hands
on your lower back for support,resting your elbows and lower arms
on the ground.Breathe deeply and hold for at the posture for at
least 5-10 breaths,increasing the hold over time .To come down,slowly
lower your legs, keeping them very straight- a little workout for
your abdominal muscle. |
 |
 |
4.The
Corpse- Savasana
Maybe the most important posture,the Corpse also known
as the Sponge,is as deceptively simple as Tadasna,the
Moutain pose.Usually performed at the end of a session,the
goal is conscious relaxation.Many people find the “conscious”
part the most difficult because it is very easy to drift
off to sleep while doing Savasana. |
Endrophine
| Source: |
http://thailabonline.com
|
|
http://yogasite.com
|
|
www.abc-of-yoga.com
|
|
www.mju.ac.th
|
|
www.healthandyoga.com
|
|
|
|